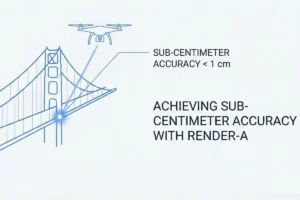
Shadows from urban landscapes can greatly affect the profitability of solar investments. Traditional 2D satellite maps often miss the complex details of city rooftops. This includes chimneys, parapets, and neighboring high-rises that block sunlight.
The introduction of 3D photogrammetry has changed urban shading analysis. It turns uncertainty into precise engineering. This technology creates detailed digital twins of urban environments. It allows for accurate assessments of solar efficiency.
Render-a leads in using 3D photogrammetry to protect solar investments. This article will explore how digital twins enhance solar efficiency. It ensures urban solar projects are both feasible and profitable.
The Challenge of Urban Solar Planning
Urban solar planning faces significant hurdles due to city landscapes’ inherent complexities. The dense arrangement of buildings, varied roof structures, and vegetation create environments that impact solar energy capture.
Complex Urban Environments and Solar Potentials
Urban areas pose unique challenges for solar energy production. The close proximity of buildings can cause shading issues, reducing solar panel efficiency.
- Dense urban canyons limiting sunlight exposure
- Varied building heights and orientations affecting solar panel efficiency
- Presence of vegetation causing shading and maintenance issues
Traditional Limitations in Shading Analysis
Traditional shading analysis methods often rely on simplified models. These models fail to capture the complexity of urban environments.
Inaccuracies in Energy Yield Predictions
This can lead to inaccuracies in energy yield predictions. Such inaccuracies can result in underperformance of solar installations.
The limitations in traditional shading analysis underscore the need for advanced and accurate methods. Techniques like 3D photogrammetry are essential for improving urban solar planning.
Understanding 3D Photogrammetry in Solar Engineering
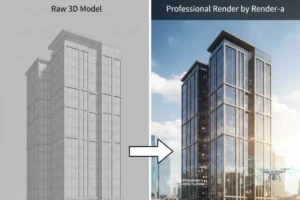
3D photogrammetry has revolutionized solar engineering, allowing for precise analysis of urban shading. This technology enables the creation of accurate 3D models of urban environments. It’s a game-changer for solar engineers.
What is 3D Photogrammetry?
3D photogrammetry extracts information from overlapping photographs to create detailed 3D models. It accurately represents complex urban landscapes. It captures the geometry and texture of buildings and terrain.
Evolution of Photogrammetry Technology
Photogrammetry technology has seen significant advancements. It has moved from manual interpretation of aerial photographs to sophisticated software-driven processes. Modern 3D photogrammetry uses advanced algorithms and machine learning for better accuracy and efficiency.
Applications in Urban Planning
In urban planning, 3D photogrammetry is invaluable. It’s used for creating digital twins, urban development projects, and infrastructure planning. It offers a detailed view of urban environments, aiding in informed decision-making.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
The benefits of 3D photogrammetry over traditional methods are numerous:
- Higher accuracy in representing complex urban geometries
- Ability to capture detailed textures and features of urban landscapes
- Enhanced efficiency in data collection and processing
- Improved decision-making through realistic 3D visualizations
By using 3D photogrammetry, solar engineers and urban planners can achieve more accurate shading analysis. This leads to optimized solar panel placement and better energy yield predictions.
The Science Behind Accurate Shading Analysis
Grasping the science behind shading analysis is essential for optimizing solar panel placement. It’s vital to accurately assess the solar energy of urban areas. This ensures solar panels are placed to capture the most energy possible.
Solar Path Modeling
Solar path modeling is a cornerstone of shading analysis. It simulates the sun’s movement across the sky at various times and seasons. This helps predict shading patterns on solar panels. By accurately modeling the solar path, engineers can pinpoint shading issues and optimize panel placement.
Shadow Casting in Complex Environments
Urban settings are complex, with buildings, trees, and other obstacles casting shadows on solar panels. Advanced tools can simulate these shadow patterns in complex environments. They consider the detailed urban landscape.
Seasonal Variations and Their Impact
Seasonal changes greatly affect shading patterns due to the sun’s path variations. Accurate shading analysis must account for these changes. This ensures solar panels work efficiently in all seasons. Understanding seasonal shading impacts helps engineers design better solar systems.
In conclusion, the science of shading analysis encompasses solar path modeling, shadow casting in complex environments, and seasonal impacts. By applying these scientific principles, solar engineers can optimize panel placement. This maximizes energy yield.
Render-a’s Advanced 3D Photogrammetry Solutions
Render-a is transforming urban shading analysis with its innovative 3D photogrammetry solutions. It uses advanced optical metrology to deliver precise data for solar engineering needs.
Technology Overview
Render-a’s 3D photogrammetry technology captures detailed spatial information. It creates accurate digital models of urban environments. This technology is essential for understanding complex urban topographies and their effects on solar radiation.
Key Features and Capabilities
The main features of Render-a’s 3D photogrammetry solutions include:
- High-resolution data capture
- Advanced image processing algorithms
- Integration with various software platforms for seamless data analysis
These capabilities allow for precise shading analysis. This is vital for optimizing solar panel placement and predicting energy yield.
Technical Specifications
Software and Hardware Integration
Render-a’s solutions are designed to work with a variety of software and hardware systems. This makes them versatile and applicable in various solar engineering projects. The technical specifications include:
- Compatibility with major CAD software
- Support for high-resolution imagery
- Advanced data processing capabilities
This integration ensures Render-a’s 3D photogrammetry solutions can be effectively used at different stages of solar project development. This ranges from planning to execution.
Methodology: Creating Digital Twins of Urban Environments
To create accurate digital twins of urban environments, a detailed methodology is used, incorporating advanced technology. This process is vital for urban shading analysis and boosting solar efficiency.
Data Acquisition Process
The initial step involves data acquisition, where technologies like LiDAR and photogrammetry are used to gather detailed urban landscape information. This includes capturing aerial imagery and LiDAR data to form a complete dataset.
- Aerial imagery capture
- LiDAR data collection
- Ground-based data collection for supplementary information
Merging LiDAR with Photogrammetry
The gathered data is then merged using advanced software. This combines LiDAR and photogrammetry strengths, creating a precise 3D urban environment model.
- Data alignment and registration
- Merging of LiDAR point clouds with photogrammetric data
Point Cloud Processing and Refinement
The merged data forms a dense point cloud. It is then processed and refined to eliminate noise and irrelevant data, ensuring a clear, accurate digital twin.
Quality Assurance Protocols
To guarantee the digital twin’s quality, strict quality assurance protocols are followed. These include:
- Data validation checks
- Accuracy assessment against ground truth data
- Visual inspection for anomalies or defects
The creation of digital twins through this methodology allows for precise urban shading analysis. It aids in better planning and optimization of solar energy harvesting in complex urban settings.
3D Modeling for Precise Urban Representation
Detailed 3D models of urban areas enable more accurate shading analysis and solar assessment. These models are created through several key processes. They ensure a precise representation of the urban environment.
Building Geometry Reconstruction
Accurate building geometry reconstruction is essential in 3D modeling for urban representation. This involves capturing the exact dimensions and shapes of buildings. It includes complex architectural features.
Vegetation and Obstacle Modeling
Vegetation and other obstacles that could affect solar radiation are modeled in detail. This includes trees, foliage, and man-made structures. They can cast shadows or reflect light.
Surface Material Properties
Understanding the material properties of urban surfaces is critical for accurate solar analysis. Different materials have varying reflectance and absorption properties. These properties affect how they interact with solar radiation.
Level of Detail Considerations
The level of detail in 3D modeling must be carefully considered. It’s a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. Too little detail can lead to inaccurate analysis. Too much detail can be computationally intensive.
By achieving a balance in detail and accurately modeling building geometry, vegetation, and surface materials, 3D modeling is a powerful tool. It provides precise urban representation in solar analysis.
Ray-Tracing Simulations: Predicting Energy Yield
High accuracy in predicting energy yield is now possible with ray-tracing simulations. This cutting-edge technology has revolutionized solar analysis. It offers detailed insights into solar panel performance across various environments.
How Ray-Tracing Works in Solar Analysis
Ray-tracing simulations model light paths as they interact with solar panel components. This includes panels, surrounding structures, and vegetation. Accurate simulation of these interactions predicts solar irradiance absorption by panels.
- Modeling complex urban environments
- Simulating the effects of shading and reflections
- Accounting for seasonal variations in solar irradiance
Calculating kWh Production with Precision
Ray-tracing simulations’ precision enables accurate kWh production calculations. This is vital for solar engineers and investors. They need to predict energy yield over a solar installation’s lifetime.
- Detailed modeling of solar panel systems
- Accurate simulation of environmental factors
- Reliable prediction of energy production
Accounting for Reflections and Diffuse Light
Ray-tracing simulations excel in accounting for reflections and diffuse light. These elements greatly affect solar installation energy yield. Accurate modeling ensures their proper consideration.
Ensuring ray-tracing simulation accuracy requires validation against real-world data. This involves comparing predicted energy yield with actual production from operational solar installations.
Validating ray-tracing simulations allows solar engineers to refine their models. This enhances prediction accuracy. It also optimizes solar installation design and performance.
Comparative Analysis: 2D vs. 3D Planning Methods
The transition from 2D to 3D photogrammetry is transforming urban solar analysis. This change is essential for precise and dependable solar assessments in complex urban settings.
Limitations of Traditional 2D Approaches
2D planning methods face significant challenges in urban solar analysis. They struggle to capture the intricacies of urban landscapes, resulting in simplified solar assessments.
- They cannot accurately account for complex building geometries and their shading effects
- They fail to incorporate detailed vegetation and obstacle modeling
- They are limited in predicting seasonal variations and their impact on solar energy production
Financial Risks of Inaccurate Predictions
Inaccurate solar assessments pose substantial financial risks for solar projects. Overestimating solar capacity can lead to underperformance, causing financial losses.
ROI Improvements with 3D Photogrammetry
3D photogrammetry significantly enhances the ROI for solar projects. It offers precise solar assessments, optimizing panel placement and reducing financial risks.
Case Studies and Success Metrics
Case studies highlight 3D photogrammetry’s effectiveness in boosting solar project ROI. For example, a study in an urban area showed a 25% improvement in solar assessments over 2D methods.
- Case Study 1: Urban Solar Farm – 3D photogrammetry improved solar assessment by 25%
- Case Study 2: Commercial Rooftop Solar – 3D photogrammetry reduced financial risks by 30%

Ideal Applications and Target Users
The use of 3D photogrammetry in solar engineering is revolutionizing how urban planners and energy investment companies tackle solar project development. This technology shines in sectors needing exact shading analysis and solar capacity evaluation.
Solar Engineering Firms
Solar engineering firms greatly benefit from 3D photogrammetry. They use detailed 3D models of urban settings for thorough shading analysis. This optimizes solar panel placement for peak energy output.
Urban Planners and Architects
Urban planners and architects also see significant gains from 3D photogrammetry. It allows them to craft urban spaces that better capture solar energy. They can seamlessly integrate solar panels into building designs.
Energy Investment Companies
Energy investment companies increasingly turn to 3D photogrammetry for solar project viability assessments. It offers precise energy yield forecasts, aiding investors in making sound solar project investment choices.
Implementation Requirements
Effective 3D photogrammetry implementation demands specialized software and hardware for capturing and processing high-resolution 3D data. Knowledge in photogrammetry and solar engineering is also critical for accurate data interpretation.
A leading expert in the field notes, “The future of solar engineering hinges on the precise analysis of urban environments via 3D photogrammetry. This enables more efficient and effective solar project development.”
“The integration of 3D photogrammetry into solar engineering marks a significant step forward in the renewable energy sector.”
Future Developments in 3D Photogrammetry for Solar Analysis
Emerging trends in 3D photogrammetry are significantly improving solar energy assessments. As technology advances, we anticipate major breakthroughs in this field.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
The fusion of AI and machine learning algorithms is poised to transform 3D photogrammetry. A report by
“the global AI in energy market is expected to grow significantly, driven by the need for efficient energy management systems.”
This expansion will likely influence 3D photogrammetry, leading to more precise and efficient solar analysis.
Real-Time Analysis Capabilities
Future advancements will concentrate on real-time analysis, enabling more dynamic solar energy planning. This will empower decision-makers to act on the latest data.
Integration with Smart City Initiatives
As cities evolve, 3D photogrammetry will increasingly integrate with smart city projects. This integration will enhance urban planning, incorporating solar energy into city infrastructure seamlessly.
Render-a’s Research and Development Roadmap
Render-a is committed to advancing 3D photogrammetry technology. Our roadmap includes improving AI, speeding up data processing, and broadening software compatibility. Our CEO notes,
“We are dedicated to pushing the boundaries of what is possible in solar analysis.”
Conclusion: Transforming Urban Solar Planning with Advanced Technology
The integration of 3D photogrammetry in urban solar planning has transformed the field. It enables more accurate and efficient solar assessments. This technology creates detailed digital twins of urban environments. It allows for precise shading analysis and energy yield predictions.
As urban areas grow, optimizing solar energy production becomes more critical. With 3D photogrammetry, solar engineering firms, urban planners, and energy investment companies can make better decisions. This reduces financial risks and improves return on investment.
To explore the latest advancements in 3D photogrammetry and its applications in urban solar planning, connect with
Render-a on LinkedIn, YouTube. Stay updated on the latest technologies and innovations.