Are You Using the Right 3D Modeling Software for Your Business?
The choice of 3D modeling software has become one of the most critical decisions for professionals working in architecture, real estate, construction, and creative industries. With the evolution of technology in recent years, the landscape of available tools has expanded significantly, yet many practitioners still rely on outdated platforms or struggle to find solutions that truly align with their specific project requirements. The question is no longer simply which software exists, but rather which platform delivers the performance, versatility, and integration capabilities that today’s demanding workflows require. Experience the difference for yourself without any commitment. To help you find the perfect fit for your workflow, we invite you to try our application for free. You can explore all the professional features and high-performance tools immediately by using our pre-loaded demo project.
Understanding the Current Market for 3D Rendering Solutions
The professional 3D rendering market has undergone remarkable transformation. Industry professionals now expect their software to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, from initial conceptualisation through final output. The best 3D modeling software in 2026 must support not only traditional modelling capabilities but also real-time rendering, cloud collaboration, and integration with emerging technologies such as drone measurement and automated surveying.
When evaluating 3D modeling software, professionals must consider several fundamental factors. These include the learning curve required for team implementation, the cost structure relative to project budgets, compatibility with existing workflows, and most importantly, the quality of output that the software can produce. The software landscape has shifted toward solutions that provide comprehensive ecosystems rather than single-purpose tools.
Industry Standards Shaping the Best 3D Modeling Software
Several industry standards have emerged that define what constitutes professional-grade 3D modeling software. The first standard involves rendering capability. Modern 3D rendering engines must deliver photorealistic output without sacrificing rendering time excessively. The second standard addresses accessibility. Cloud-based solutions and collaboration features have become non-negotiable for teams distributed across multiple locations. The third standard encompasses integration capabilities, particularly with drone technology and automated measurement systems that provide accurate spatial data for modelling projects.
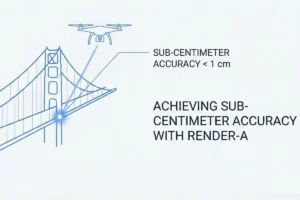
Professionals in architecture and construction increasingly rely on drone-based surveying and measurement techniques to inform their 3D models. This integration between physical measurement technology and digital modelling has created a new category of requirements for software platforms. Solutions that can seamlessly incorporate drone measurement data have become industry essentials rather than optional features.
Top Characteristics of Leading 3D Modeling Platforms
The leading 3D modeling software solutions available in 2026 share several common characteristics that distinguish them from entry-level alternatives. Firstly, they provide intuitive user interfaces combined with powerful underlying processing capabilities. Professionals can achieve complex results without requiring months of training for basic proficiency.
Secondly, the best platforms offer real-time collaboration features that allow team members to work simultaneously on the same project from different locations. This capability has become particularly valuable as studios and design firms increasingly embrace hybrid and distributed working models.
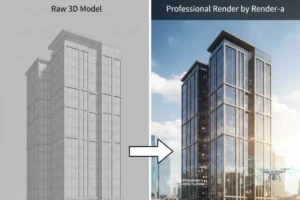
Thirdly, professional-grade software includes advanced rendering engines that produce publication-quality output. These engines utilise sophisticated algorithms for light calculation, material simulation, and physical accuracy. The rendering quality directly impacts client satisfaction and project success rates.
Fourthly, integration with complementary technologies defines modern standards. Solutions that connect with 3D modeling solutions from render-a and similar platforms demonstrate how professional software now functions within broader technological ecosystems. This integration approach ensures that data flows seamlessly between surveying equipment, modelling software, and final rendering platforms.
The Role of Drone Technology in Modern 3D Modeling
Drone technology has fundamentally altered how 3D modelling projects begin. Professional surveyors now use drone measurement to capture precise spatial data, creating point clouds and orthophoto maps that serve as foundations for accurate digital models. The best 3D modeling software accommodates this workflow by providing native support for the data formats generated by drone surveying equipment.
Companies utilising professional drone roof survey services can now directly import measurement data into their modelling platforms, eliminating manual data conversion steps that previously consumed considerable time and introduced potential errors. This integration of drone measurement technology with 3D modeling software represents a fundamental industry shift toward greater accuracy and efficiency.
Evaluating Software Options for Your Specific Needs
Selecting the best 3D modeling software requires honest assessment of your specific project requirements rather than simply choosing the most popular option. Different platforms excel in different domains. Some software specialises in architectural visualisation, others in product design, landscape rendering, or real estate marketing.
The evaluation process should consider the following elements:
- The primary output type required for your projects, whether architectural renderings, product visualisations, or environmental analysis
- The scale of projects you typically handle, from single rooms to complex urban environments
- Your team size and the necessity for collaborative features
- Integration requirements with existing tools and workflow processes
- Budget constraints both for initial software acquisition and ongoing subscription costs
- Training requirements and the availability of educational resources
- Hardware specifications available within your organisation
Honest evaluation across these dimensions helps narrow the field to solutions genuinely suited to your circumstances rather than those that merely appear impressive in marketing materials.
Understanding 3D Rendering as a Service Model
An important trend in professional 3D modeling involves the transition toward software as a service models combined with rendering-as-a-service platforms. Rather than relying entirely on local hardware for processing, professionals increasingly leverage cloud-based rendering services that produce high-quality output while reducing demands on internal computational resources.
The render-a approach to 3D modeling solutions exemplifies this evolution, providing integrated platforms where modelling, collaboration, and rendering services function as cohesive systems. This integration eliminates the need to juggle multiple standalone tools and ensures consistency throughout the entire project lifecycle.
Practical Considerations for Implementation
Implementing new 3D modeling software across a professional organisation requires thoughtful planning. The transition period inevitably involves reduced productivity as team members develop proficiency with new tools and interfaces. Organisations should budget adequate time for this learning curve and consider running parallel systems during transition periods until teams demonstrate confidence with new platforms.
Technical support quality becomes particularly important during implementation phases. Software vendors that provide comprehensive documentation, tutorial resources, and responsive support teams significantly reduce implementation friction and accelerate the team’s path to full proficiency.
Integration testing should occur before full rollout. Confirming that the new software functions correctly with your existing systems, hardware configurations, and workflow processes prevents frustrating surprises after implementation begins. Testing should specifically include drone measurement data import and any other specialised requirements relevant to your operations.
Future Directions in 3D Modeling Technology
The trajectory of 3D modeling software development points toward several emerging capabilities. Artificial intelligence increasingly assists with repetitive modelling tasks, material assignment, and even preliminary design generation based on reference images or brief descriptions. Augmented reality integration allows clients and stakeholders to visualise 3D models within real-world environments before final approval.
Real-time ray tracing capabilities continue to improve, enabling interactive exploration of fully-rendered environments rather than static final images. This shift toward real-time rendering fundamentally changes how professionals present work and how clients engage with design proposals.
Integration with IoT sensors and live environmental data enables 3D models that reflect actual real-world conditions. Architectural models could automatically adjust lighting based on current weather, or structural analysis could incorporate live load data from monitoring sensors.
Building Your Professional 3D Modeling Ecosystem
Rather than viewing 3D modeling software in isolation, successful professionals build integrated ecosystems that combine modelling, rendering, drone measurement, collaboration, and delivery platforms into coherent workflows. This ecosystem approach eliminates data silos and reduces the friction points that typically slow project delivery.
The best approach involves selecting a core modelling platform that genuinely suits your primary work type, then deliberately integrating complementary tools rather than attempting to force one package to handle all requirements. This strategy provides flexibility to upgrade individual components as technology evolves without requiring wholesale replacement of your entire toolkit.
For professionals in real estate, architecture, and construction, this ecosystem should specifically include drone surveying capabilities and the ability to import drone measurement data directly into your modelling platform. Companies offering comprehensive drone roof survey services paired with integrated 3D modeling solutions represent the current industry standard for spatial data collection and digital visualisation.
Industry Resources and Continued Learning
Professional development in 3D modeling software continues throughout your career as technologies evolve and new capabilities emerge. Following industry leaders and organisations on professional networks helps you stay current with emerging tools and best practices. The render-a team maintains presence on YouTube with regular educational content and shares insights across professional networks that help practitioners remain informed about advancing capabilities in drone measurement, 3D rendering, and integrated workflow solutions.
Investing in ongoing training and professional development creates significant competitive advantages. Professionals who understand not only how to use specific software but why particular tools excel in specific contexts consistently deliver superior results and maintain stronger client relationships.
Choosing Your Path Forward
The best 3D modeling software for your practice ultimately depends on your specific project types, team structure, budget parameters, and integration requirements. Rather than pursuing the most expensive or most hyped option, select software that genuinely aligns with your actual workflows and delivers superior output in your particular domain.
Modern professional practice increasingly requires 3D rendering capabilities that extend beyond traditional modelling into areas like drone measurement integration, real-time collaboration, and cloud-based rendering infrastructure. The software platforms leading the industry in 2026 excel because they recognise these interconnected requirements and provide unified solutions rather than asking practitioners to cobble together disconnected tools.
As you evaluate options, prioritise platforms that integrate seamlessly with drone-based surveying technology, provide intuitive interfaces that minimise training overhead, offer rendering capabilities that produce genuinely impressive results, and support the collaborative workflows that define contemporary professional practice. The investment you make in selecting appropriate software pays dividends throughout your project pipeline, from initial data capture through final client delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between 3D modeling software and 3D rendering software?
3D modeling software focuses on creating and manipulating three-dimensional geometric forms and structures. You use these tools to build digital representations of physical objects or environments. 3D rendering software takes completed models and processes them through sophisticated algorithms to generate photorealistic images or animations. Many modern platforms integrate both capabilities, allowing seamless workflow from model creation through final 3D rendering output. The distinction matters when evaluating tools because some platforms excel more at one function than the other.
How does drone measurement integrate with 3D modeling software?
Professional drone measurement systems capture precise spatial data including orthophoto maps and point clouds. Modern 3D modeling software accepts these data formats directly, allowing you to import drone-collected information as foundations for accurate digital models. This integration streamlines workflow significantly because surveyors can capture spatial data efficiently, and modellers can work from verified measurements rather than relying on approximations. Platforms offering native support for drone measurement data eliminate manual conversion steps and reduce opportunities for measurement errors.
Is cloud-based 3D rendering preferable to local processing?
Both approaches offer distinct advantages depending on your circumstances. Local processing provides complete control and works effectively when you have substantial hardware investment and need frequent iteration with rapid feedback. Cloud-based 3D rendering distributes computational load to powerful remote infrastructure, reducing demands on your local systems and often producing faster results for complex scenes. The optimal approach frequently combines both methods, using local software for initial modelling and collaboration, then leveraging cloud rendering services for high-quality final output. This hybrid strategy balances control with efficiency.
What should I prioritise when selecting 3D modeling software for my team?
Begin by identifying your primary output requirements. What types of models do you create most frequently? Evaluate the learning curve required to bring your team to proficiency. Examine integration capabilities with tools already in your workflow, particularly drone measurement systems if you work in surveying or construction. Consider scalability as your projects grow. Assess whether the software supports the collaborative features your distributed team requires. Finally, verify that support resources including documentation and training materials meet your team’s learning style preferences. Honest evaluation across these dimensions produces better outcomes than simply choosing the most expensive or most popular option.
How often should professionals update their 3D modeling software?
Most professional 3D modeling software platforms follow annual or semi-annual update cycles introducing new features and performance improvements. You should evaluate updates based on whether they address your specific workflow requirements. Major version updates often warrant more thorough testing before full team implementation, whereas minor updates typically present minimal disruption. Establish a schedule for periodic software assessment, perhaps annually, examining whether newer versions of your current platform or alternative solutions better serve your evolving project types and team structure. Remaining current with updates generally provides better support and security, but update timing should align with your project schedule to avoid implementation during critical work periods.